Whenever you use Google, you probably type the phrase you want into the search bar, tap enter, and then the magic happens! Since you are reading this blog post, you probably already know a bit more than average about how a search engine works.
But since it’s always good to review, here are 6 advanced commands to help you get the most out of guest posts, discover unused internal linking opportunities, and reveal duplicate content.
Do you know the uses of Google Advanced Search? It can help you improve your searches and deliver hyper-focused results using search operators (or their combinations). For example, you can search for articles published by a competitor last week or discover internal linking opportunities that you missed. Surprised? Learn all the advanced tricks hidden in the Google algorithm!
First, repeat after me: I am lazy.
And don’t say otherwise. Laziness may not be a virtue, but it does have an advantage: it makes you look for creative ways to get something done without spending a lot of time doing it. Working on SEO, I am always looking for ways to get stuff done without working overtime.
In short, I want to work smarter, not harder. How do I do it? I look for tools, tactics, or even tricks that will save time and allow me to get the job done faster. Senuto is a natural choice when it comes to my daily grind, but I will share a few other tips in this article.
One of my favorite tricks? Google Advanced Search
But what is it? In simple terms, Google Advanced Search helps you customize your search to find exactly what you are looking for. This is an extremely useful skill, especially if you want to extract tiny and specific pieces of information quickly.
A quick mini-course in advanced search operators
Let’s start from the beginning. To keep things simple, let’s stick to 4 operators that I, as an SEO guy, use all the time.
The first one is the most popular search operator “SITE:”. It allows you to limit the results to one domain. Just enter site:[site name] in Google. Example: site:https://www.senuto.com/en/
For example, if I enter site:https://www.senuto.com/en/, I will only see results for Senuto:
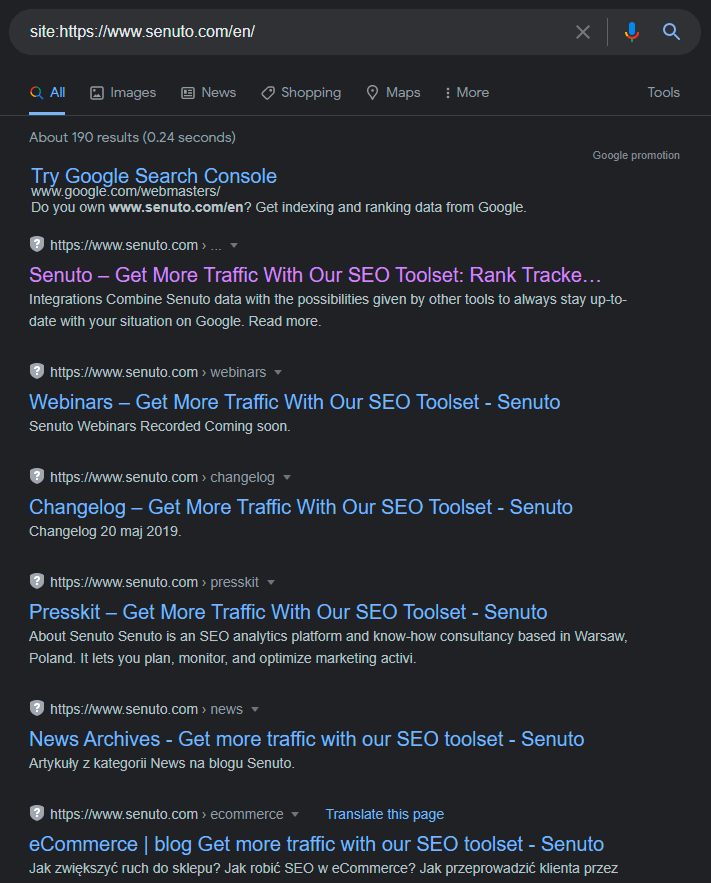
Remember that you don’t have to enter the http://, https:// or www. prefixes with this operator. But that’s not all. You can add a keyword to this operator to see if the particular page has the relevant content.
Let’s say I want to check if a page contains the keyword “infographic”. I type site:https://www.senuto.com/en/ infographic and get this result:
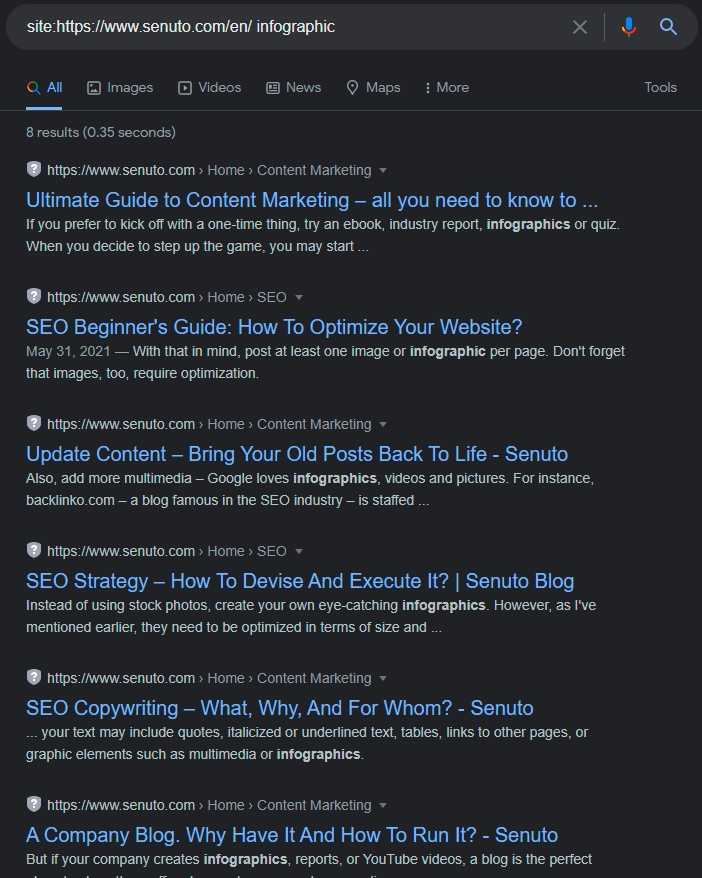
I use this operator a lot because it allows me to limit my search to one domain. Remember it, because we will continue to make it work for us.
Another useful operator is the quotation mark (“”), letting us get an exact match. It limits our search to the exact phrase only. For example, below we have a normal Google search (note the number of results):
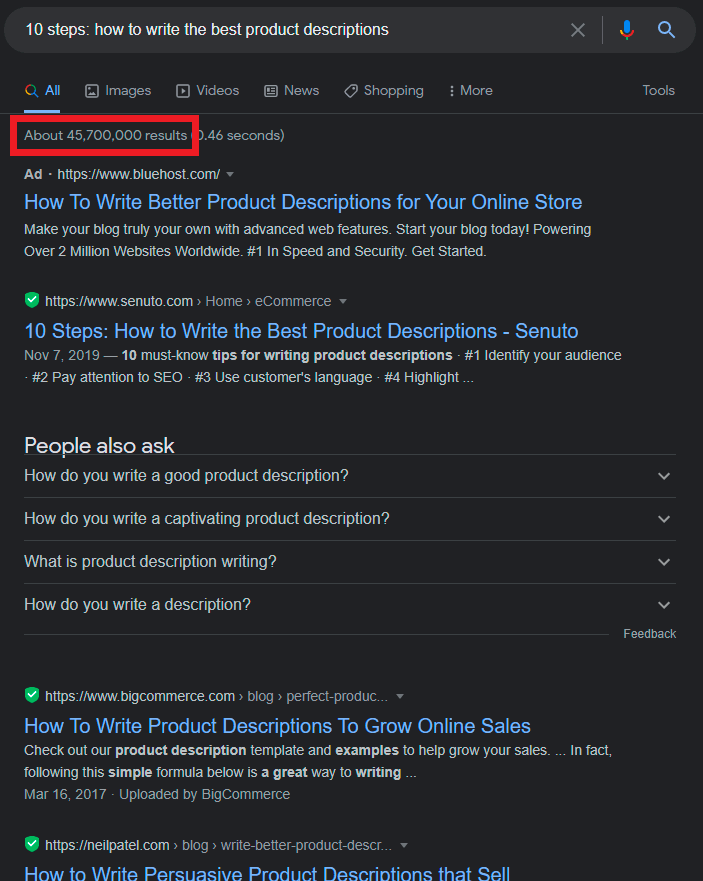
And now we put the same phrase in quotation marks:
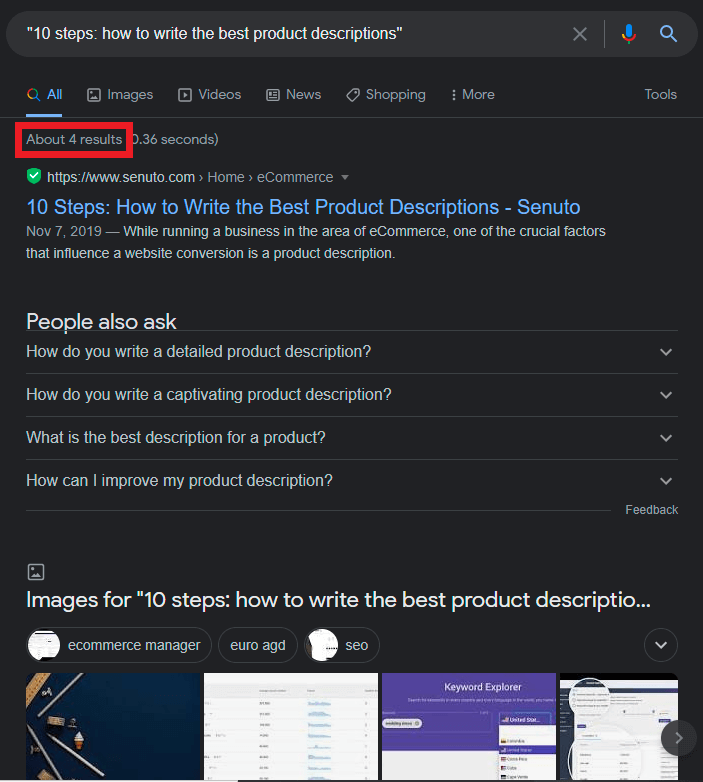
The difference speaks for itself.
Unlike normal search, an exact match will only show results where the keyword appears in the same form as in the quotation marks. This operator is especially useful when looking for duplicate content on the page, which may negatively affect your rankings (more on that in a moment).
Finally, we have the minus (-) and plus (+) operators for precise searches. The minus (-) operator excludes certain keywords from the results. So, if I want to read articles from Senuto’s blog, but not ones about SEO, I enter the following formula:
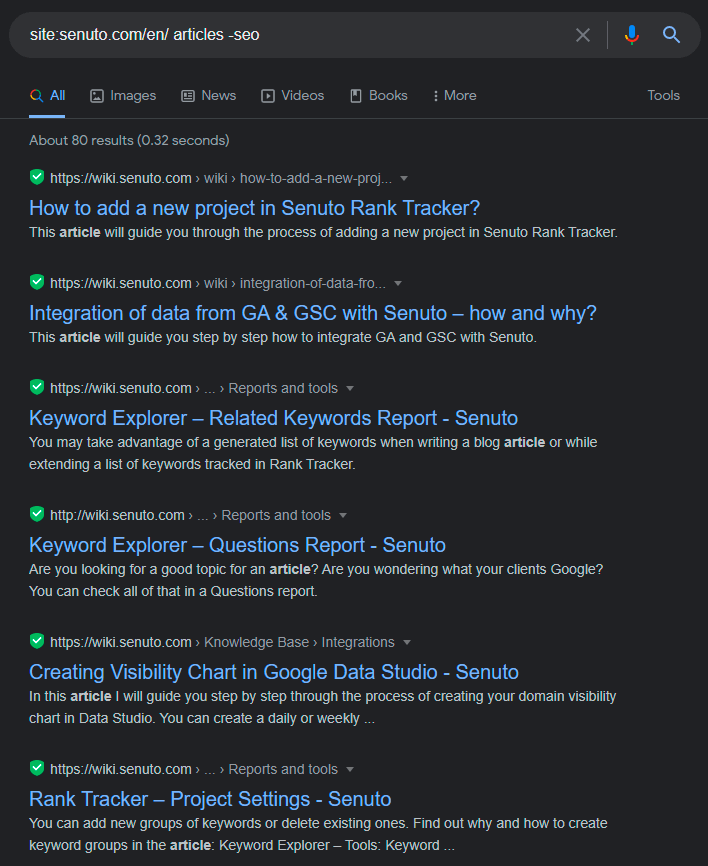
By typing -seo, I will only get results for articles, not SEO. The plus operator (+), as you may have guessed, works inversely. By using it, you can add words to your search phrase, altering the results.
For example, in the Google search engine, I entered the following query:
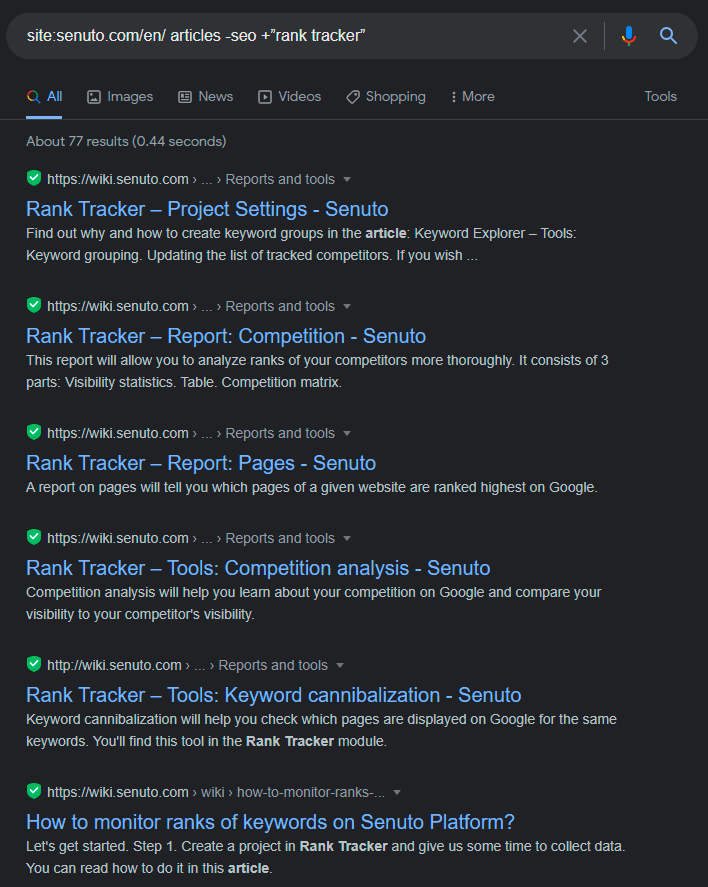
So what happened here? I used the site:, minus, and plus operators to find articles on Senuto’s blog which are related to the Rank Tracker, but not to SEO.
There are many search operators (too many to list here…). To keep things simple, this tutorial will stick to the following operators: site, quotation marks, minus, and plus.
6 tips for Google Advanced Search to improve SEO
By applying these Google Advanced Search operators, you can find exactly what you are looking for while spending less time on searching. Advanced Search can be useful especially if you are just starting your adventure and want to deal with everything by yourself. It’s easier than you think, just watch:
1. Simple but insightful googling of the competition
Googling your competition is very easy. Just use the operator related: and page url. Related: displays pages that are, well, related to a specific web address. This operator not only allows you to identify direct competitors, but also indirect, peripheral competitors that you may have overlooked in your search. But there’s more! The operator related: helps you understand how Google categorizes your and your competitors’ pages.
Let’s check what Google finds if we look for competitors related to, for example, the popular database of businesses PKT.pl.
We type related:pkt.pl in the search bar and we see the following list:
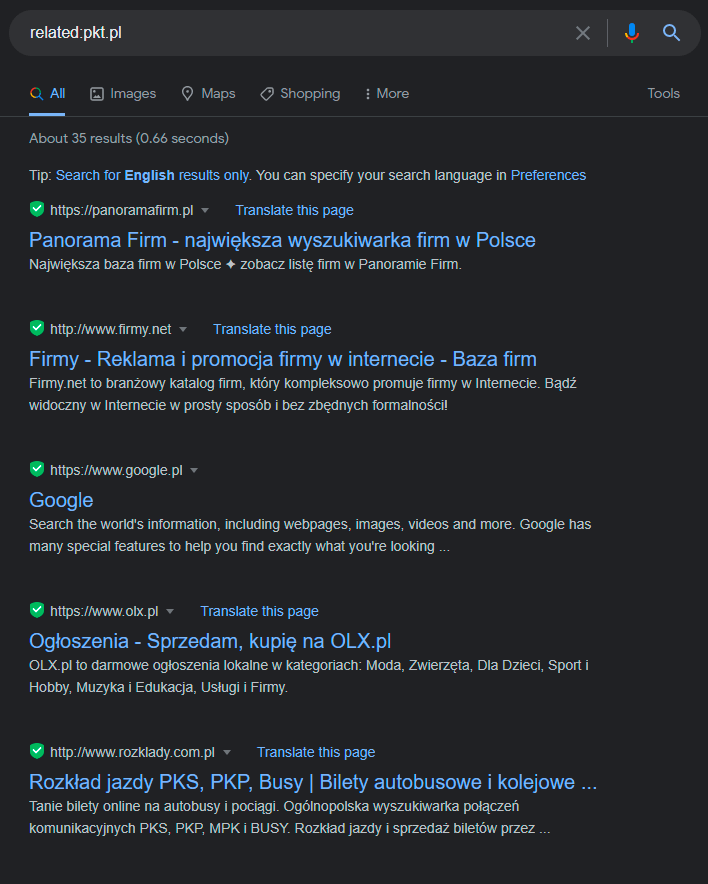
This example shows that Google considers itself an associated resource – and being one of the largest databases of companies on the web, it is definitely right.
Of course, this is a down-and-dirty, basic method for identifying competition or related websites, but it’s worth a shot – it’s fast, free, and always at your fingertips when you want to know what the search engine sees and how it associates resources.
2. Track your competitors’ content management strategy
Time to track your competition from home. Here’s an easy way to spy on their content management strategy: combine the operator site: and Google’s date filter.
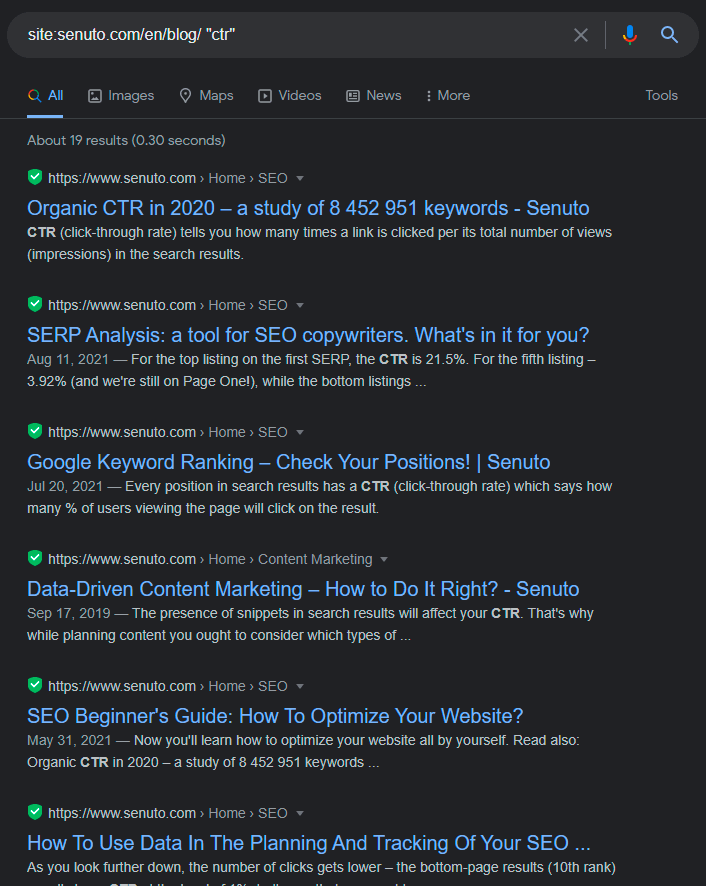
To limit my searches to just the blog, I will look at the subpage senuto.com/en/blog by itself instead of the entire page. The difference is, CTR is mentioned 21 times throughout the website, and only in 19 resources on the blog. I can use the date filter (click on tools and select the date filter) to check what was published in the last month. Here are the results:
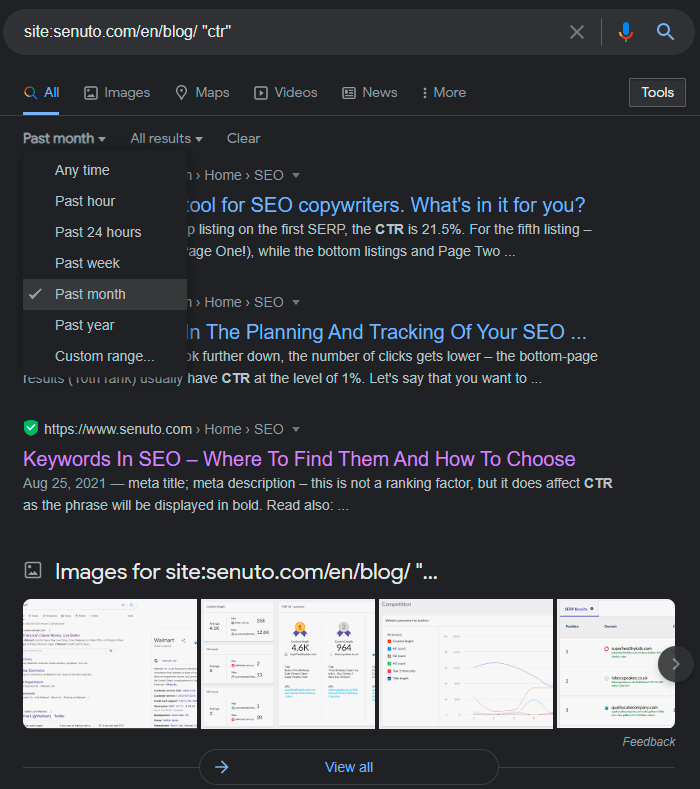
We see that the latest article containing the phrase “CTR” was posted on August 25.
This method is worth using to analyze our competitors activity. Let’s use a phrase that both we and our competitor aspire to. When you use the operator site: in combination with a date filter, Google gives you information about:
- how much content the competitor posted,
- how often they publish new content in a given period,
- what content is published at a specific time,
- how often the given topic is addressed.
Cool, isn’t it?
3. Discover the mother lode of opportunities offered by guest posts
If your goal is to drive valuable traffic to your website, gain powerful links, and raise your domain’s ranking on Google, be sure to try guest posts.
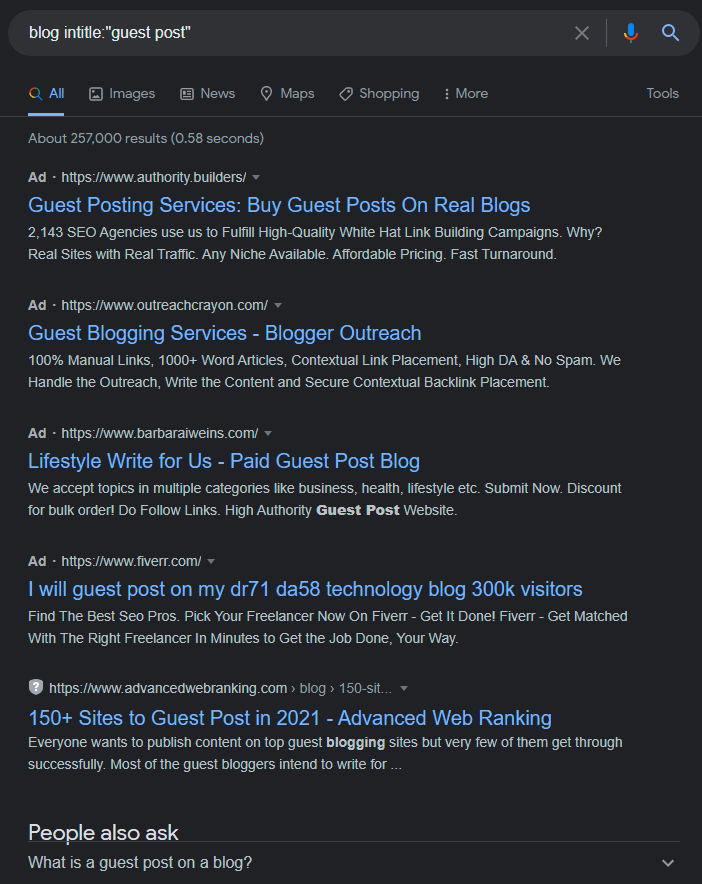
Yes, there are a million ways to start guest posting, and the most popular one is commercial, but guest blogging still works, even in 2021. There are still websites and blogs out there that will gladly accept good content from guests, as an exchange or simply a way of expanding content.
Here are some sample queries you can copy into Google:
- keyword “guest posting opportunities”
- keyword “guest post”
- keyword “submit guest post”
- keyword “guest post submission”
- keyword intitle:”write for us”
- keyword intitle:”guest post guidelines”
When looking for guest posts for automotive websites, I use the following query:
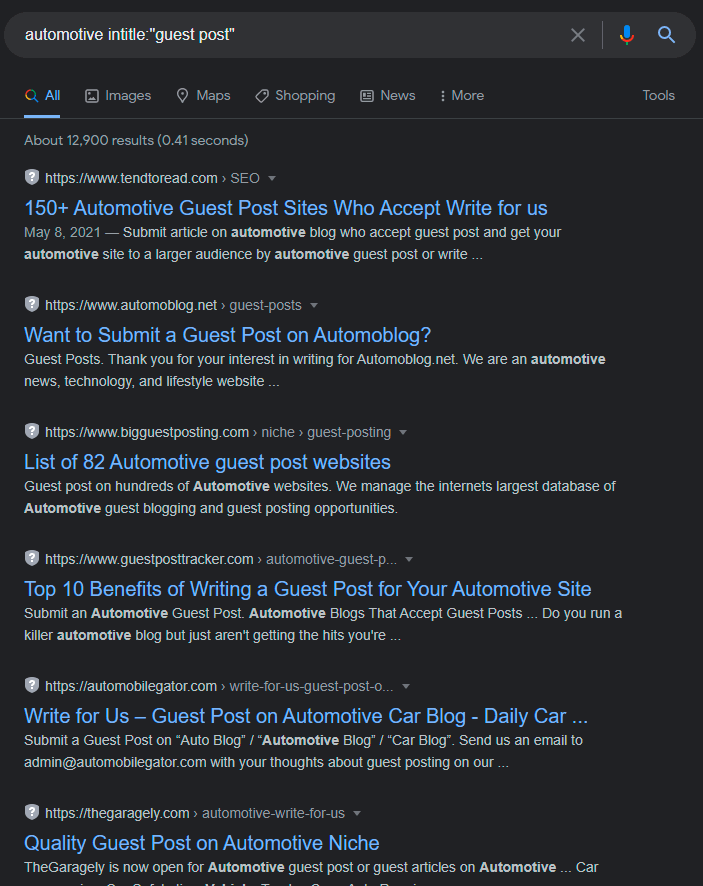
This is a free list, I just need to browse it and get to work.
And yes, perhaps it would be faster to buy an article on a well-known content publishing portal ????, but working at the grassroots level and lowering costs is what many beginner SEO people and micro-business owners need to do, so this opportunity is dedicated to them.
4. Discover the possibilities of internal linking
Internal linking plays an underexplored, but certainly important role in Google rankings. No matter how well-designed your website is, an elaborate internal linking structure can improve traffic management by redirecting visitors from one blog post to another.
Internal linking also builds topic relevance, creating content that supports the main topics of your website. So how to use the free benefits of Google, polishing your internal link juice? Just use the operator site: and a keyword in quotation marks:
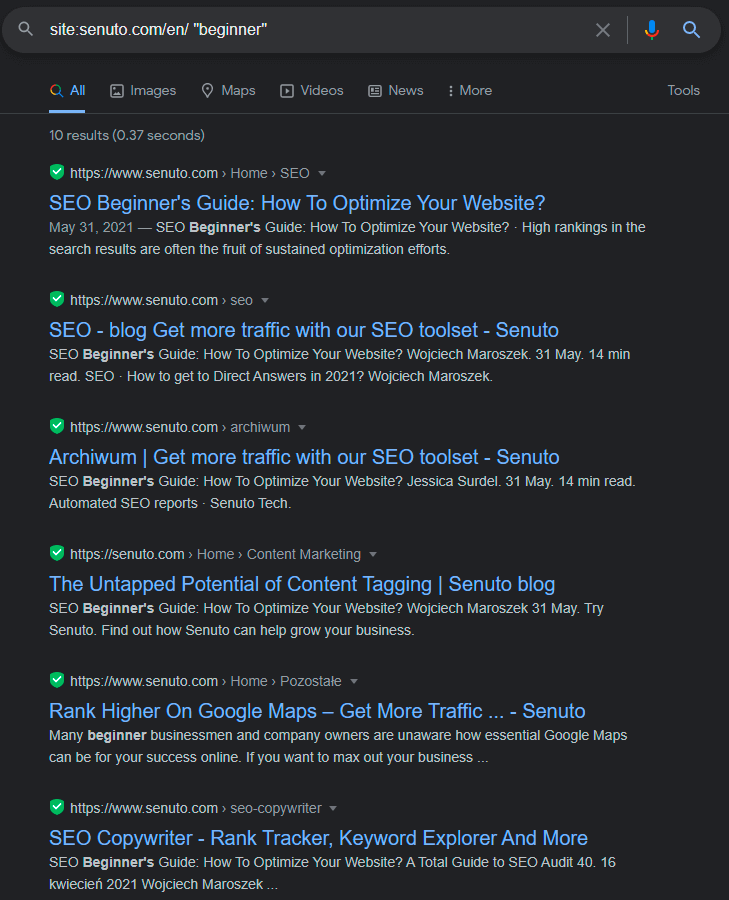
Voilà! With a simple search, I found 10 internal linking possibilities. All it took was a few seconds. You can use the following query:
site:www.yoursite.com/blog intext:”your keyword”
to get a similar effect. While this trick won’t be as useful if you’ve recently started blogging, it’s handy if you’re already managing an indexed blog that has a lot of existing content.
5. Find duplicate content on your website
Duplicate content is content that appears more than once on your page and can mislead search engines when ranking search results. In short: duplicate content is likely to lower your website rankings and is a common SEO problem that can’t be ignored. I will illustrate duplicate content by looking at how apples are described at a particular greengrocer’s site.
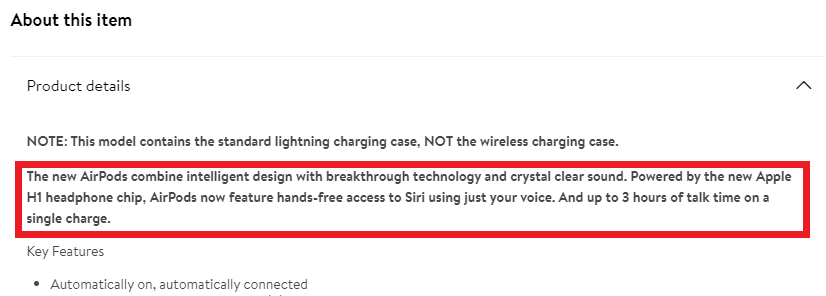
Using the operator site:, I copy a fragment of the description into Google, putting it in quotation marks. Here are the results:
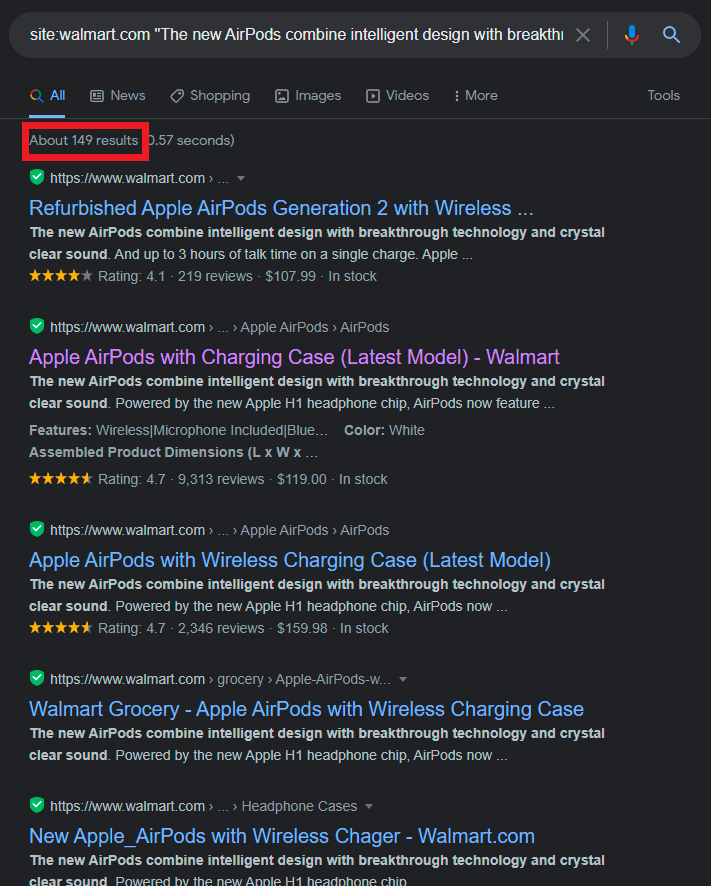
The same fragment appears on 149 subpages (!). This is not a good thing, but with stores of this size, eliminating duplicate content is a challenge. If we search for the same fragment on the entire web (not only on the analyzed page), we can see how many additional copies made their way outside.
Duplicate content is a big problem especially for blogs with thousands of pages or store pages that share the same product descriptions.
6. Discover missed content
One of the last operators I will cover is filetype:. It helps you find content that is not in HTML but in Word documents, PDF files, and the like. Such content is valuable but not optimized for search. And Analytics doesn’t show the traffic it generates.
To use this operator, just enter site:yoursite.com filetype:pdf, like so:
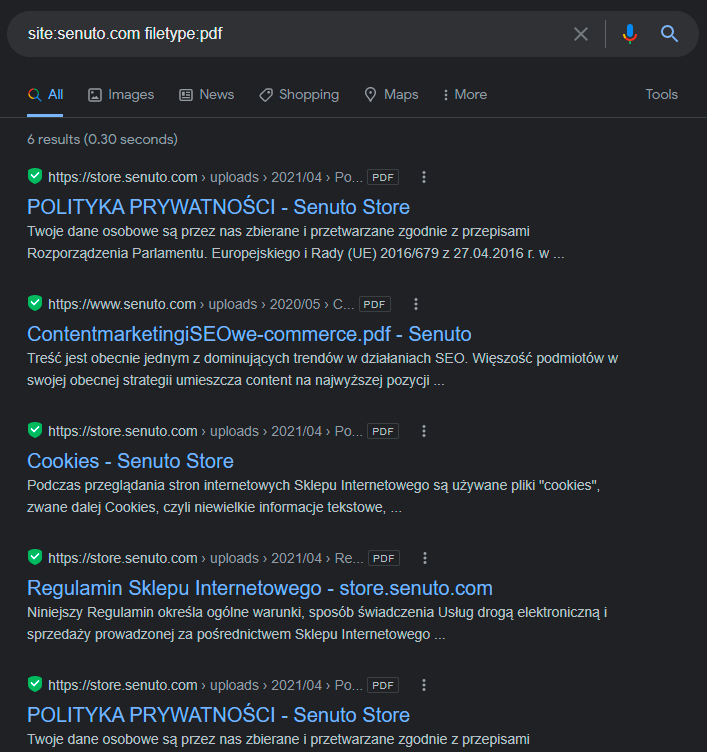
Then check this content. Have you published it as HTML? Is the search optimized? Is it possible to turn it into a valuable, high-ranking, and traceable website?
PDF files are often hidden and are generally complementary resources. They should always be a (print and download friendly) alternative to HTML content. They should never be the only version you have.
And this is just the tip of the googleberg…
I have described literally a handful of the most popular commands available in the Google search engine. This is just a starter, because Google has more power and possibilities than you might think. If you know what to look for and how to do it with advanced search operators, you can harness the true power of Google and as a result… things are awesome.
Working on SEO consists of SEO testing, tinkering with Google’s algorithm, and staying on top of recent search trends. Google Advanced Search is not only an interesting skill that you can learn in one day. It will help you discover the possibilities that are right under your nose and increase the efficiency of your work.
Google Advanced Search – a true revelation
Google is and always will be free. Knowing how to hone your searches will help you become better at SEO and bring you potential long-term benefits.
Of course, you can always take a shortcut, leave the advanced search to self-taught enthusiasts, and answer all your questions with the Senuto tool.
The choice is yours.
 Łukasz Lewczuk
Łukasz Lewczuk